
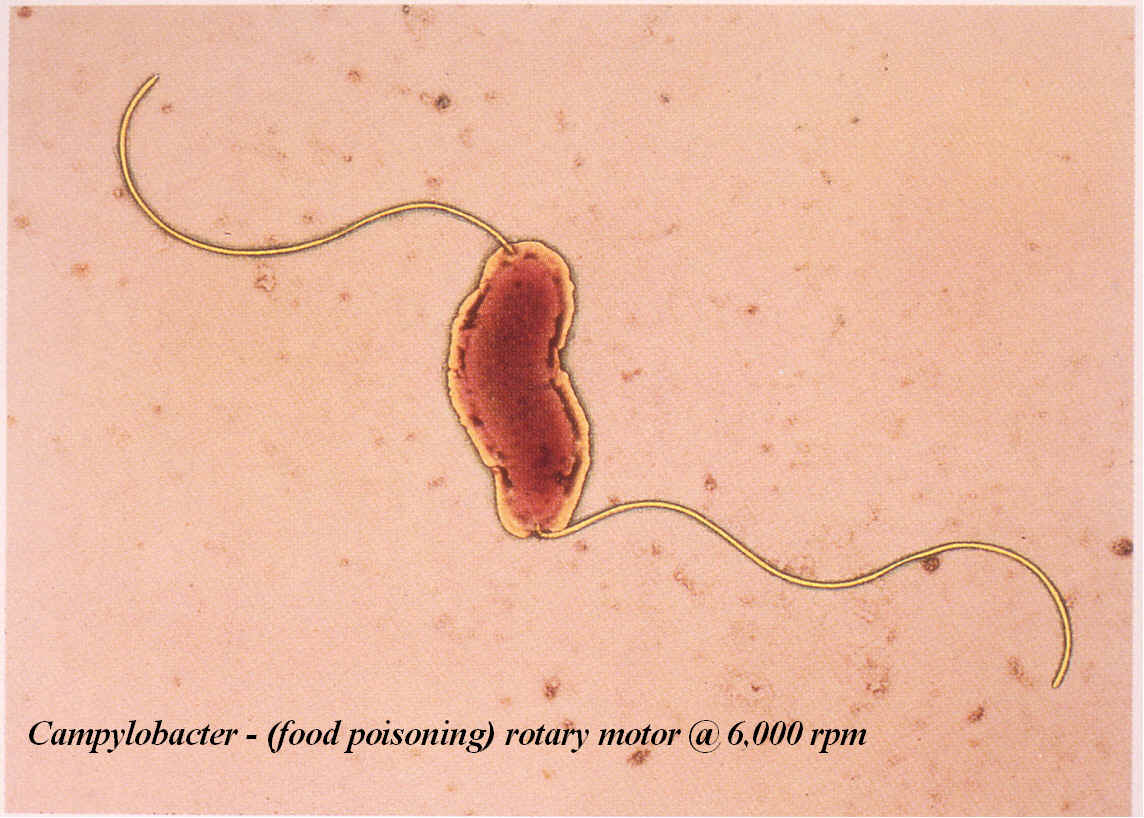
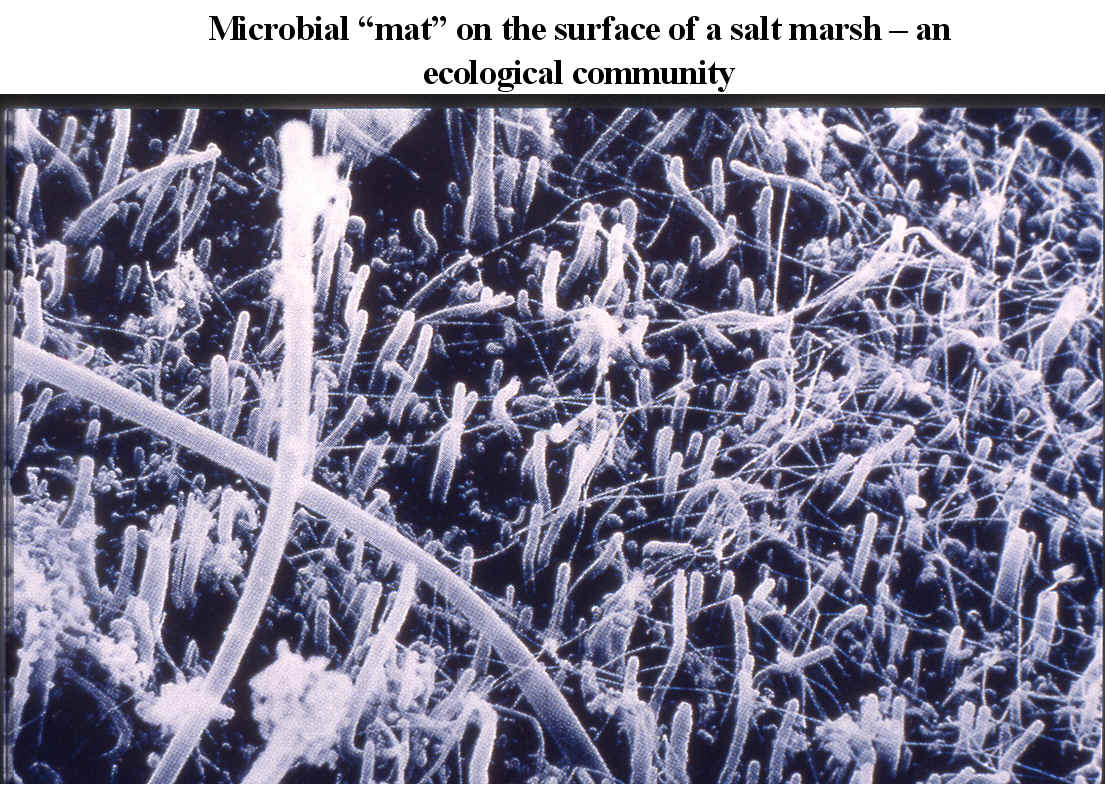

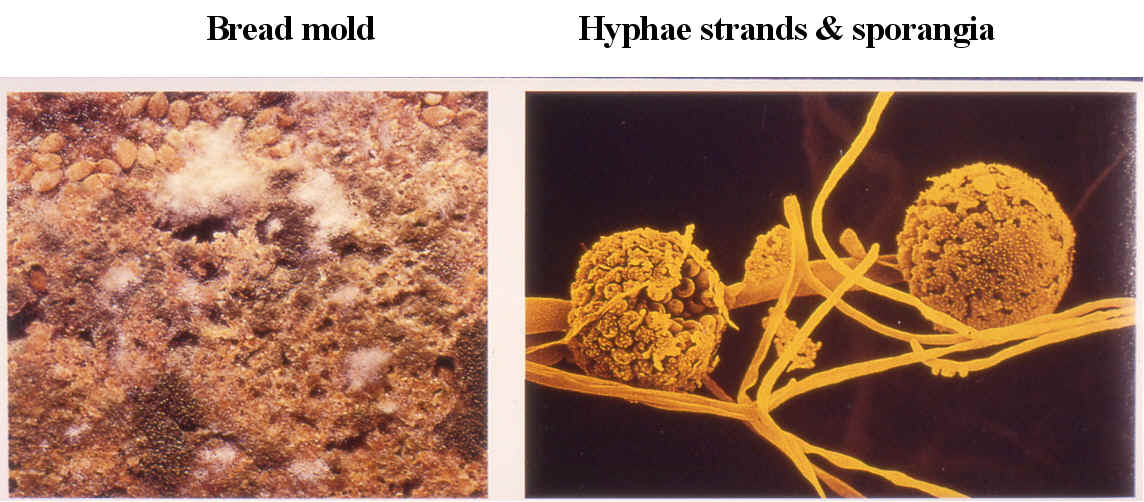
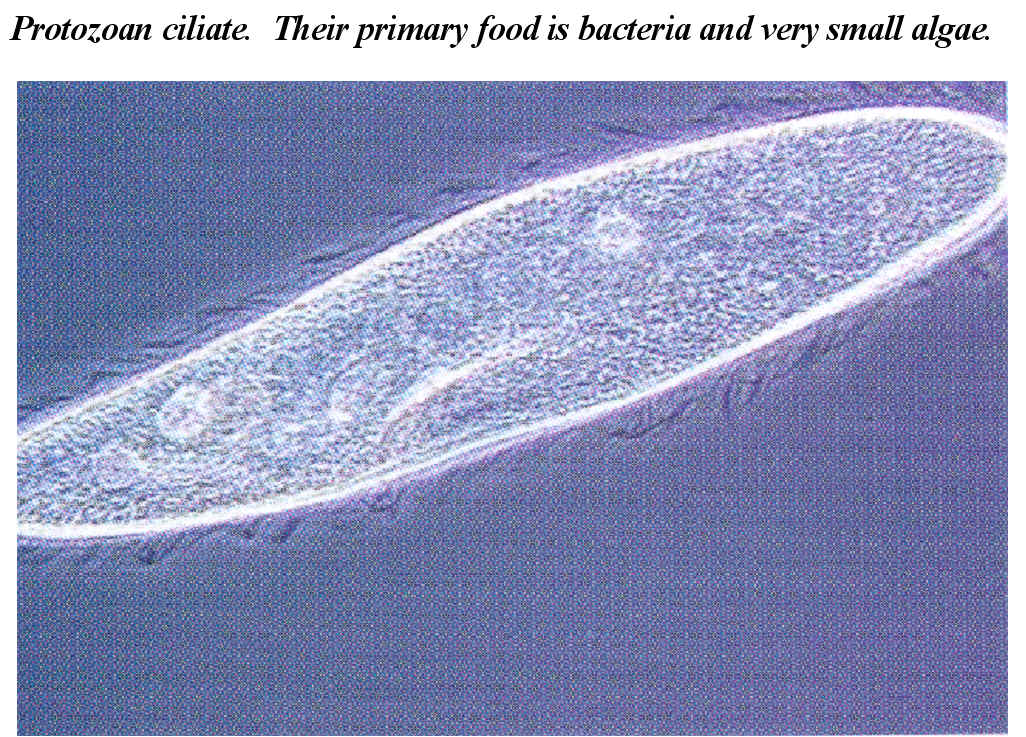
REVIEW SUMMARIES FOR
KLING LECTURES
Microbes:
Transformers of Matter and Material
1. Take home message:
"Microbes can do anything they want, wherever they
want. Without microbes, humans
wouldn’t be alive."
2. Main Terms:
Assimilative processes
Dissimilative processes
Autotrophs: photoautotroph and chemoautotroph
Heterotrophs: photoheterotroph and heterotroph
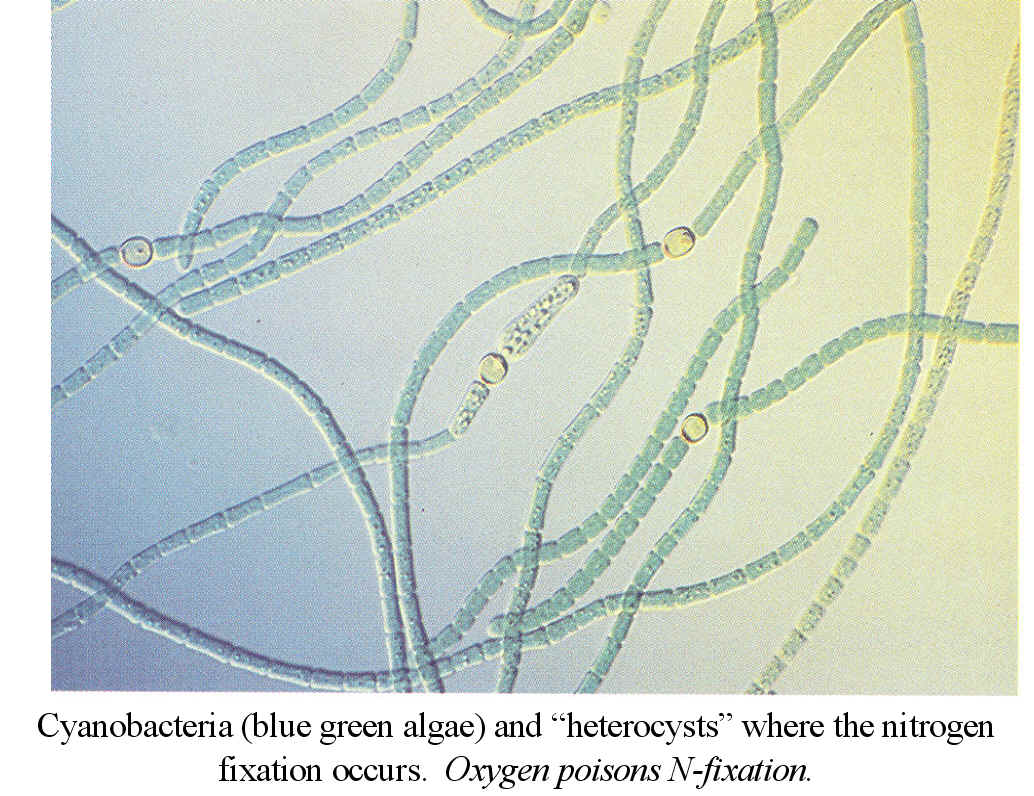
Eubacteria, Archaebacteria, Cyanobacteria (= blue-green algae)
Mycorrhizae
Decomposition or Mineralization
3. Main Concepts:
· Which organisms are included in the definition of microbes?
· How does the divergence of genetic material of the eubacteria and archaebacteria compare to the genetic similarity of plants and animals?
· What are the main biological characteristics of bacteria and fungi (consider their “diversity” of form and function).
· How do bacteria "make a living"; what are the processes they use to gain energy for growth?
· What are “reduction-oxidation” reactions; give some examples of redox reactions and how they are used by organisms (see table of 4 examples of reactions).
· Understand and be able to describe the important impacts of microbes on ecosystems:
1. Generate oxygen
2. Nutrient recycling
3. Nitrogen fixation
4. Allowing herbivores to consume poor quality food
5. Aiding plant roots in access to soil nutrientsFigures from Dusenbury:
Dusenbery, D. B. 1996. Life at Small Scale - the Behavior of Microbes. Scientific American Library, W. H. Freeman and Company, New York. 214 pp.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|